The World Bank recently approved a loan to the Government of Karnataka for projects in Bengaluru. The project is called “Karnataka Water Security and Resilience Program” and is financed under the instrument called “Program for Results” (PforR). You can find the main document as well as environment and social impact assessments in this dataset. In this explainer we will go into details of the project and what is expected to be covered.
How much is the funding?
The total project is expected to cost USD 677.0 million, or Rs. 5754.5 Crores. Note that this more than a quarter of BBMP’s 2025-26 budget.
Of this amount, World Bank is financing USD 426 million, or Rs. 3621 Crore, the Karnataka government will finance USD 246 million, or Rs. 2091 Crore, and the remaining USD 5 million, or Rs. 42.5 Crore, is to be raised through private capital.
Who is going to be the Implementing Agency?
The Revenue Department, Government of Karnataka, Bangalore Water Supply and Sewerage Board (BWSSB), and the Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP) are to be the implementers.
What is the project?
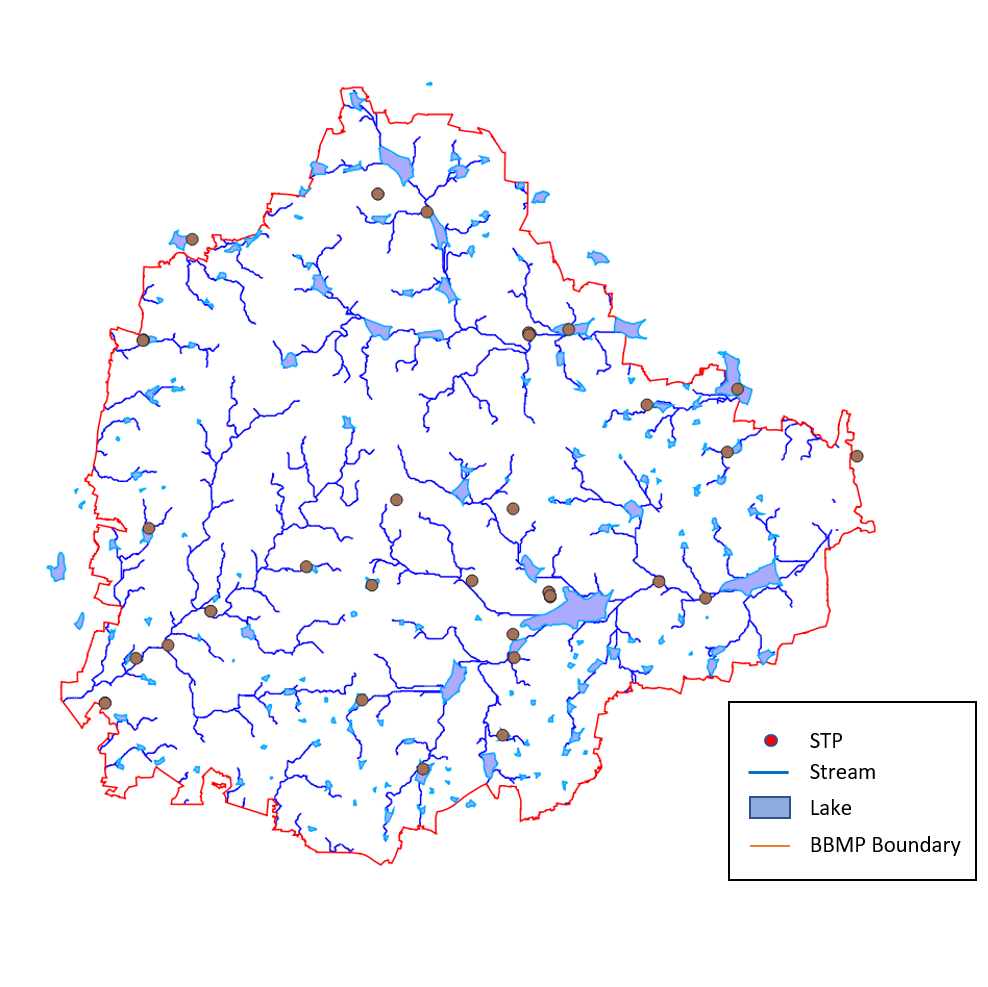
The program aims to improve two things – water security and flood resilience of Bengaluru. It aims to solve the issues of flooding related disasters by improving the stormwater drain (SWD) network and the interconnected lakes network. Lakes holding excess rain water are expected to help water security through ground-water recharge and other means.
The Program is expected to enable access to sanitation for 2 million people and mitigate climate risks like flooding for 4 million people. For this, the project has three Result Areas (RAs).
RA1: Improving infrastructure and services for enhanced water security and resilience
RA1 will focus on water, sanitation, drainage, and Disaster Risk Management (DRM) infrastructure, and services that directly enhance resilience to floods and droughts. BBMP will be incentivised to fully integrate SWDs to lakes to create “climate-resilient balancing reservoirs”. These lakes can be used to retain and release water for groundwater recharge, recreation, and green zones along with stormwater management.
| Activity | Funds |
| Strengthening and integrating SWDs, lakes, and NBS in a flood management system will improve resilience to floods. | USD 84 million Rs. 714 Cr |
| Operationalizing scaled circular economy investments and removing raw sewage from SWDs will improve water availability and public health outcomes. | USD 40 million Rs. 340 Cr |
| Total | USD 124 million Rs. 1054 Cr |
RA2: Strengthening institutions and integrated planning
The goal is to improve integrated planning across agencies, strengthening institutions, and reforms in disaster risk governance.
Integrated planning will involve:
- Water audits for 16 sub-basins across Karnataka
- A comprehensive water security plan for greater Bengaluru
- Detailed sub-catchment flood management plans for Bengaluru informed by advanced flood modelling
Institutional approach to SWDs will be through setting up eight zonal (for the eight zones in BBMP), multi-agency SWD cells. These cells will have the following charter:
- Develop O&M implementation plans, with citizen engagement, behavior change campaigns, and a new digital water and environmental governance system.
- The plan will also monitor, track and benchmark critical sector indicators for treated waste water –
- effluent from sewage treatment plants (STPs),
- STP utilization rate,
- water reuse
- industrial and residential wastewater effluent, residential water harvesting structures
- develop a lake health index.
- An effluent treatment plant for industrial wastewater will be installed to remove toxic materials and chemicals in a high-pollution industrial zone.
- Nature-based solutions (NBSs) will also be demonstrated in flooding hotspots in each of the city’s eight zones.
This effort will involve multiple agencies and is expected to involve BWSSB, Karnataka State Pollution Control Board (KSPCB), BBMP’s SWD, lakes and solid waste management divisions and apply to the 860 km of SWDs.
In addition to the above, institutions will be strengthened/reformed as follows:
- Karnataka State Disaster Management Authority’s (KSDMA) capabilities for DRM will be enhanced by establishment of functional units like Mitigation and Disaster Risk Financing(DRF).
- Karnataka State Natural Disaster Monitoring Cell (KSNDMC) will be scaled up to a Centre of Excellence (CoE) focused on proactive climate actions and strategies for managing extreme weather conditions. A comprehensive new data model called the “Karnataka Climate and Multi-Hazard Risk Information System” is expected to be developed.
| Activity | Funds |
| Enhancing scientific understanding and systems for integrated flood management | USD 36 million Rs. 306 Cr |
| Institutionalizing a coordinated O&M approach for all SWDs in Bengaluru will increase water availability and climate resilience. | USD 63 million Rs. 535.5 Cr |
| Implementing reform and operationalizing DRM institutions in alignment with legal mandates and global best practice. | USD 77 million Rs. 654.5 Cr |
| Total | USD 176 million Rs. 1496 Cr |
RA3: Enhancing financial capabilities and resources of key institutions.
RA3 seeks to strengthen the financing sustainability of BWSSB and BBMP. For this purpose, the following are the goals of the result area:
- Improvement of BWSSB’s cost recovery through operational efficiencies, smart water meters for large consumers, and Non-Revenue Water (NRW or leakages) reduction.
- The program will aim to increase the revenue of BWSSB by at least 30% through Public Private Partnerships at BWSSB.
- Support to BBMP to strengthen capital investment planning and financial management systems enhancement.
- Establishment of a Disaster Risk Financing Unit and development of a state DRF strategy. The strategy can enable investment of at least USD 20 Million from private capital towards disaster financing.
| Activity | Funds |
| Increasing OSR and meeting the 2021 FBM Rules promulgated by GoK. | USD 90 million Rs. 765 Cr |
| Strengthening the financial foundation for a climate-resilient water-secure city by moving BWSSB toward creditworthiness. | USD 25 million Rs. 212.5 Cr |
| Enabling risk and resilience financing through strategic and market-based mechanisms. | USD 10 million Rs. 85 Cr |
| Front end fee | USD 1 million Rs. 8.5 Cr |
| Total | USD 126 million Rs. 1071 Cr |
Outcomes of the Project
The main Program Development Objectives (PDOs) are improving water security related municipal services, institutions and financing in Bengaluru and strengthening DRM institutions in Karnataka.
The main outcomes and indicators to measure success are as follows:
- Outcome 1: Improving infrastructure and services for enhanced water security and resilience
- Indicator 1: People with enhanced resilience to climate risks (Corporate, number, gender disaggregated)
- Indicator 2: People provided with safely managed sanitation (Corporate, number, gender disaggregated)
- Outcome 2: Strengthening institutions and integrated planning
- Indicator 3: Disaster risk governance institutional reform program implemented for KSNDMC and KSDMA.
- Outcome 3: Enhancing financial capabilities and resources of key institutions
- Indicator 4: Own source revenue increased for BBMP and BWSSB.

